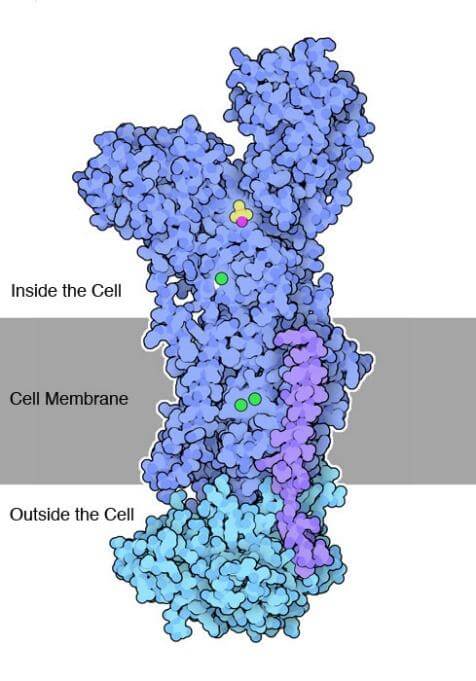
The sodium-potassium (Na+/K+) pump or Na+/K+ adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) is an electrogenic transmembrane enzyme that maintains the resting membrane potential across the cell membrane.
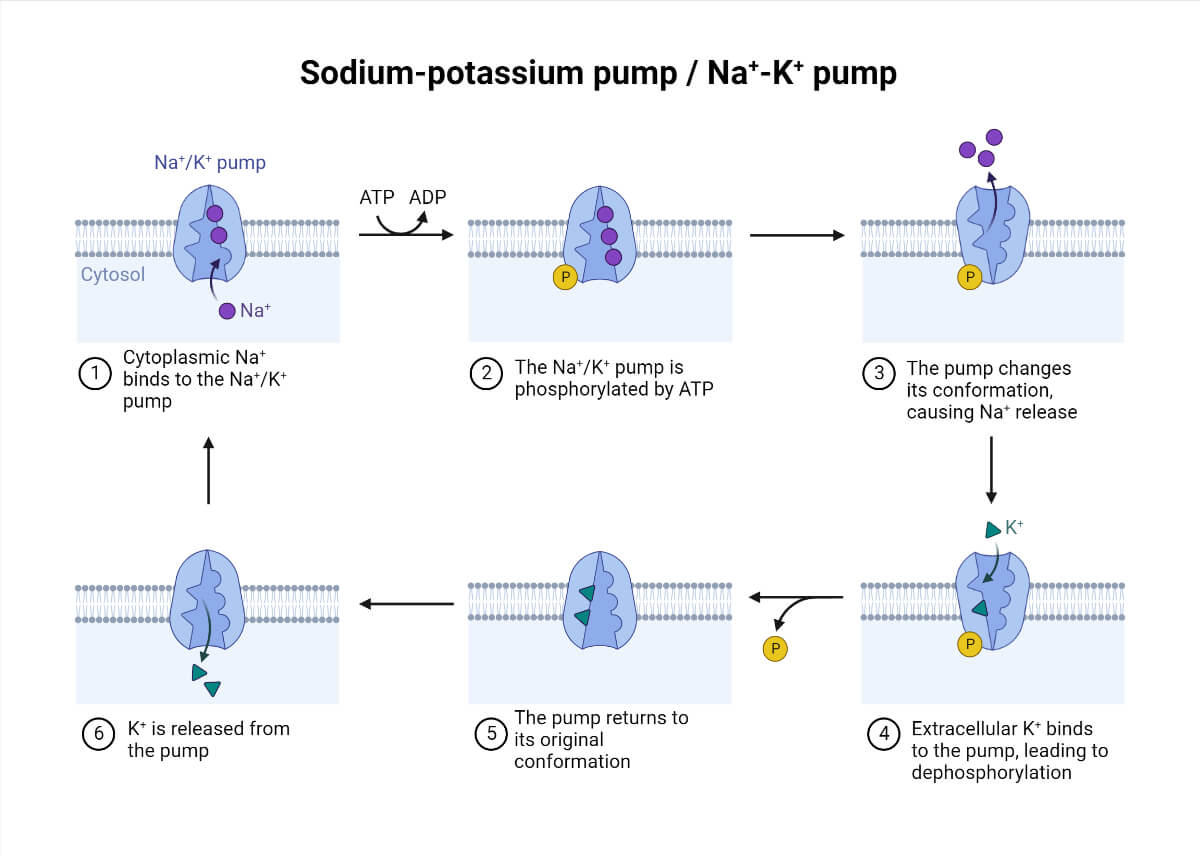
It is mostly observed in nerve cells for neurotransmission through electrical signals. It was first discovered in 1957 by the Danish scientist Jens Christian Skou, who was later awarded the Nobel Prize in 1997. This discovery improved our understanding of cell ion intake and outflow.